
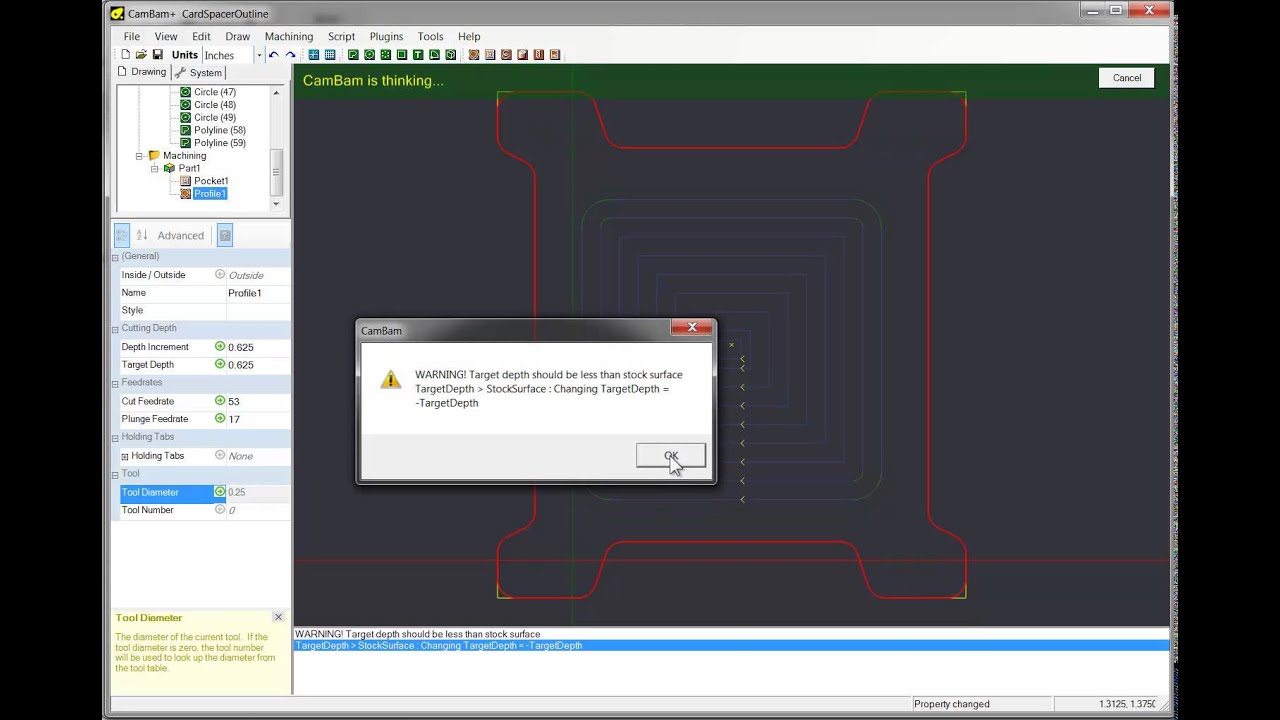
- #Cambam drops starting location of arc install
- #Cambam drops starting location of arc manual
For example, in case its section has changed since last enabling it. This does not ask the changed units to reload their own configurations (see the Reload action). See systemd.unit(5) § UNIT FILE LOAD PATH for the directories where available unit files can be found. 
Mask a unit to make it impossible to start 4
#Cambam drops starting location of arc manual
Show a manual page associated with a unitĮnable a unit to start automatically at bootĮnable a unit to start automatically at boot and start it immediatelyĭisable a unit to no longer start at boot socket can be used to check and find them. If you just installed a package, pacman -Qql package | grep -Fe.
A package may offer units for different purposes. The -now switch can be used in conjunction with enable, disable, and mask to respectively start, stop, or mask the unit immediately rather than after rebooting. Most commands also work if multiple units are specified, see systemctl(1) for more information. See also systemd/User#Basic setup to enable/disable user units for all users. To instead operate on user units (for the calling user), use systemctl -user without root privileges. The commands in the below table operate on system units since -system is the implied default for systemctl. Also, if a template unit is called without an instance identifier, it will generally fail (except with certain systemctl commands, like cat). most unit files containing an sign are meant to be templates. suffix file name, although by convention such a "clash" happens rarely, i.e. To be more accurate, before trying to instantiate the suffix template unit, systemd will actually look for a unit with the exact string. string is called the instance identifier, and is similar to an argument that is passed to the template unit when called with the systemctl command: in the unit file it will substitute the %i specifier. rvice): this means that they are instances of a template unit, whose actual file name does not contain the string part (e.g. Note: Some unit names contain an sign (e.g. device unit, therefore specifying /dev/sda2 is equivalent to vice. Similar to mount points, devices are automatically translated into the appropriate. For example, specifying /home is equivalent to home.mount. Mount points will automatically be translated into the appropriate. For example, netctl and rvice are equivalent. If you do not specify the suffix, systemctl will assume. There are however a few short forms when specifying the unit in the following systemctl commands: When using systemctl, you generally have to specify the complete name of the unit file, including its suffix, for example sshd.socket. Units commonly include, but are not limited to, services (. After installing, the module will be added under System administration. #Cambam drops starting location of arc install
Plasma users can install systemd-kcm AUR as a graphical frontend for systemctl.This will use SSH to connect to the remote systemd instance. You can use all of the following systemctl commands with the -H host switch to control a systemd instance on a remote machine.Some of its uses are examining the system state and managing the system and services. The main command used to introspect and control systemd is systemctl. 6.8 Disable emergency mode on remote machine.6.5 Short lived processes do not seem to log any output.6.4 Shutdown/reboot takes terribly long.5.4 Sandboxing application environments.5.2 Running services after the network is up.3.3 Mapping between SysV runlevels and systemd targets.Other parts include a logging daemon, utilities to control basic system configuration like the hostname, date, locale, maintain a list of logged-in users and running containers and virtual machines, system accounts, runtime directories and settings, and daemons to manage simple network configuration, network time synchronization, log forwarding, and name resolution. systemd supports SysV and LSB init scripts and works as a replacement for sysvinit. systemd provides aggressive parallelization capabilities, uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services, offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux control groups, maintains mount and automount points, and implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic. It provides a system and service manager that runs as PID 1 and starts the rest of the system. Systemd is a suite of basic building blocks for a Linux system.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
